Lecture 00 – Introduction to Embedded Systems
Course Description
In this course, students learn about hardware and software aspects of embedded systems. Students learn C programming language through use in an embedded platform. The course builds on CMPE 310, introducing advanced topics including communication interfaces, advanced IO devices and other peripherals, multitasking, firmware, real-time operating systems/embedded operating systems and device drivers. The course will provide a hands-on experience in designing and ramming an embedded system using a microcontroller-based development platform.
3 units
What is an Embedded System?
Definition: Embedded System
An embedded system is a system embedded in a larger system.
- In our context, "embedded system" will mainly refer to a microprocessor-based embedded system. It serves as the electronic control and processing unit for the system.
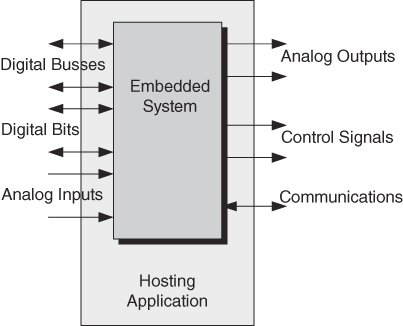
Common characteristics:
- A computer system embedded, collocated with hardware
- A system with hardware (mechanical, electrical, etc...) and a processor to run software, often with a special set of constraints such as very low power, very small, reliable, safe, secure, real-time, etc...
- To widely varying degrees, designed to perform a specialized task (reliably), in contrast to general purpose computer systems designed to be versatile and run a variety of software applications
Key Markets
- Automotive
- Consumer Electronics
- Industrial Robotics
- Medical Devices
- Military & Defense
Automotive
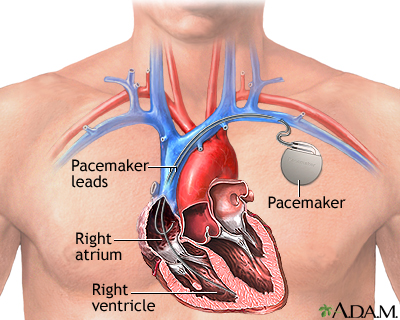
Medical
- Already self-evident that engineering can be rewarding, but must be taken seriously --- building complex systems that are reliable and safe requires mastery of disciplined approaches
- One one hand, to get initially motivated you sometimes want to avoid getting get caught up in and dismayed by the mountains of details, but you must then also motivate yourself to conquer the details to perform reliable work and produce safe results
CPS Controllers
CPS System:
- a Cyber-Physical System (CPS)
- interacts with an environment, some aspects of which it can affect
- accepts commands from an external entity (unless autonomous)
- involved in a feedback loop for control
- transducer: a device that converts variations in a physical quantity, such as pressure or brightness, into an electrical signal, or vice versa. -- Oxford
- converts one type of energy into another
- ADC: an analog-to-digial converter converts an analog signal (continous-time, continuous-variable) into a digital signal (discrete-time, discrete-valued)
- DAC: an digial-to-analog converter
- an electronic sensor typically refers to a component that contains some of type of transducer
- smart sensors: sensors can contain ADC and embedded processors packged with the transducer
- actuators: a controlable device that allows for physical control or movement
- Digital Signal Processing, the study of the maniputation of digital signals, is well-motivated by studing the equivilence of , to an
analog circuit
Security
Roots of Trust (RoT)
Highly reliable hardware, firmware, and software components that perform specific, critical security functions. Because roots of trust are inherently trusted, they must be secure by design. Roots of trust provide a firm foundation from which to build security and trust. -- https://csrc.nist.gov/glossary/term/roots_of_trust
Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
technology is designed to provide hardware-based, security-related functions. A TPM chip is a secure crypto-processor that helps you with actions such as generating, storing, and limiting the use of cryptographic keys. The following topics provide details.
source: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security/information-protection/tpm/trusted-platform-module-top-node
-
TPMs are commonly microcontrollers, and defined through software(firmware)
-
TPMs are less complex then the larger system, more tightly controlled, and (hopefully) trustworthy
-
Because TPMs are defined through software, one might instead opt for a hardware, silicon root of trust
-
reduce the attack surface and worry about only attackers that can impact the HW IC in your system
-
Example Effort: https://opentitan.org/
https://security.googleblog.com/2019/11/opentitan-open-sourcing-transparent.html :
Anchoring trust in siliconSilicon RoT can help ensure that the hardware infrastructure and the software that runs on it remain in their intended, trustworthy state by verifying that the critical system components boot securely using authorized and verifiable code. Silicon RoT can provide many security benefits by helping to:
- Ensure that a server or a device boots with the correct firmware and hasn't been infected by a low-level malware.
- Provide a cryptographically unique machine identity, so an operator can verify that a server or a device is legitimate.
- Protect secrets like encryption keys in a tamper-resistant way even for people with physical access (e.g., while a server or a device is being shipped).
- Provide authoritative, tamper-evident audit records and other runtime security services.
The silicon RoT technology can be used in server motherboards, network cards, client devices (e.g., laptops, phones), consumer routers, IoT devices, and more. For example, Google has relied on a custom-made RoT chip, Titan, to help ensure that machines in Google’s data centers boot from a known trustworthy state with verified code; it is our system root of trust. Recognizing the importance of anchoring the trust in silicon, together with our partners we want to spread the benefits of reliable silicon RoT chips to our customers and the rest of the industry. We believe that the best way to accomplish that is through open source silicon.
-
Instrumentation
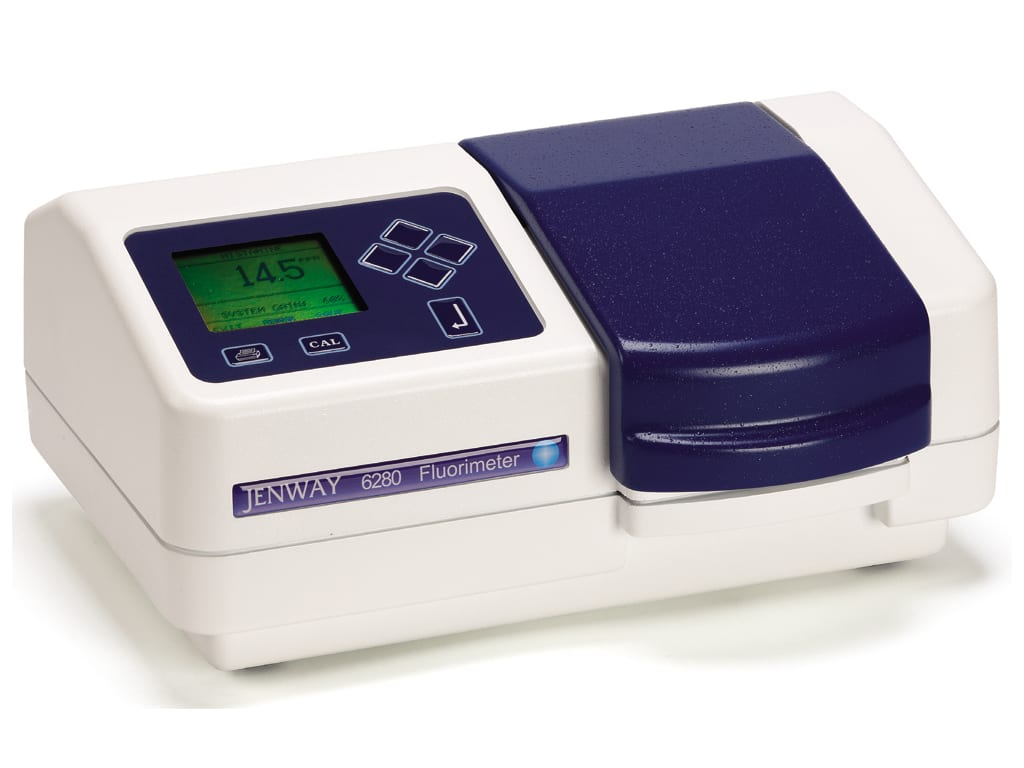
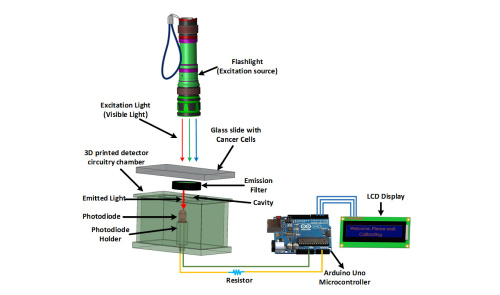
Mohammad Wajih Alam, Khan A. Wahid, Raghuveera Kumar Goel, and Kiven Erique Lukong, "Development of a low-cost and portable smart fluorometer for detecting breast cancer cells," Biomed. Opt. Express 10, 399-410 (2019)
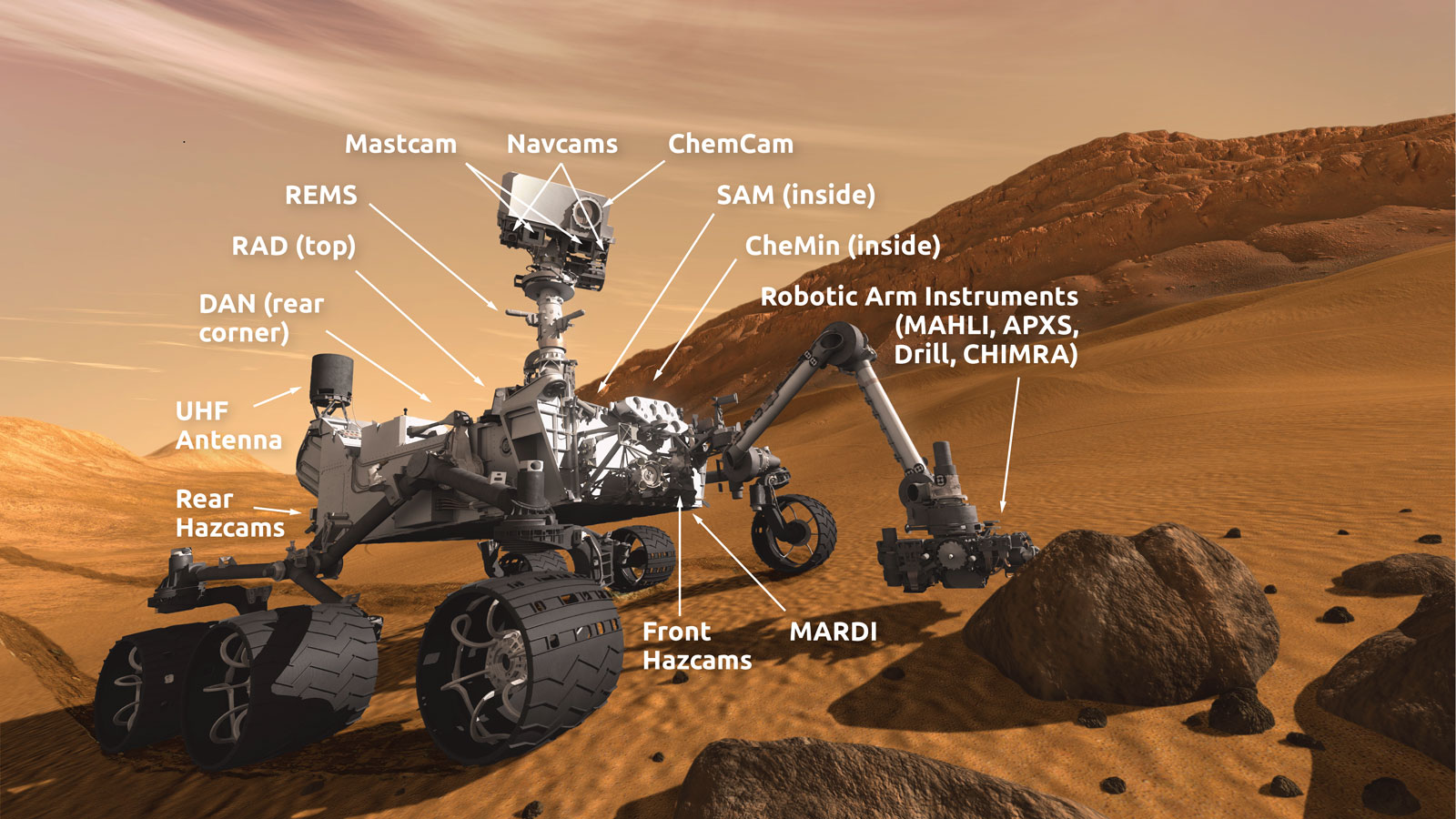
https://mars.nasa.gov/msl/spacecraft/instruments/summary/
-
Visit this link: https://mars.nasa.gov/msl/spacecraft/instruments/summary/
-
characterized by requirements
- various real-time constraints
- size
- weight
- power
- cost
- security
- environmental conditions
Why Learn Emedded Systems?
- Profitable - Large job market, driven by 10s of billons of dollars comparable to mobile processor market
- "The global microcontroller market size was valued at $16.49 billion in 2019 and is expected to reach $42.19 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 11.50% from 2020 to 2027." https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/microcontrollers-market
- Important - Critical enabler for many modern systems improving health and safety, raising quality of life, and increasing scientific knowledge
- Interesting Opportunity for Creativity - ability to provided solutions in widely variation applications, with simple solutions having real enabling impact
Implementation Technology/Devices
- General-Purpose Microprocessors
- FPGAs (Field Programmable Gate Arrays)
- SoC (System on Chip)
- DSP (Digial Signal Processors)
- ASICs (Application Specific Integrated Circuits)
- ASIP (Application-Specific instruction set Processors)
Why Microcontrollers?
- Peripheral loaded
- ADC, DAC, GPIOs, Serial Interfaces
- Cheap
- ~$1 for 8-bit processor
- Low Power
- ~300μA operation (1 AA battery for 275 days)
- <1μA sleep (1 AA battery for 225 years)
- Programmable
- Assembly or C
- Overall, versitile and inexpensive
- https://www.digikey.com/en/blog/sub-dollar-microcontrollers-turn-the-embedded-world-upside-down
Sub-Dollar Microcontrollers Turn the Embedded World Upside Down
- https://www.digikey.com/en/blog/sub-dollar-microcontrollers-turn-the-embedded-world-upside-down
Google Shopping Jan 2022
Common Varients:
- 8-Bit Microcontroller
- 16-Bit Microcontroller
- 32-Bit Microcontroller
Why AVR?
Our Microcontroller
- AVR Butterfly
- ATMEGA 169PV chip
- Built-in peripherals
- 120 segment LCD Screen
- Joystick
- Piezo element – sounds
- Programmer
- AVR Dragon
- These boards will be used for projects and discussions

- Easy-to-learn instruction set
- The instruction set of the AVR is one of the simplest to learn, which makes debugging and examining trade-offs at the level of disassembly approachable
- Abstraction is the key to digital system design, and creativity is key in engineering. Learning to build with a simple 8-bit microcontroller reinforces and developes skills and intuition for invention.
Our Book (Required)
https://bcs.wiley.com/he-bcs/Books?action=index&bcsId=11853&itemId=1119457505

Embedded Systems: A Contemporary Design Tool, 2nd Edition by James K. Peckol, Publisher: John Wiley & Sons,Inc. (a.k.a. Wiley),
ISBN-13: 978-1119457503
ISBN-10: 1119457505
Provided Lecture Notes
Note: Throughout this course, lectures and provided slides do not encompass all material in the course. They are meant to be complementary and not a substitute for reading material and HW.
Diagram of a Microprocessor-based Embedded System
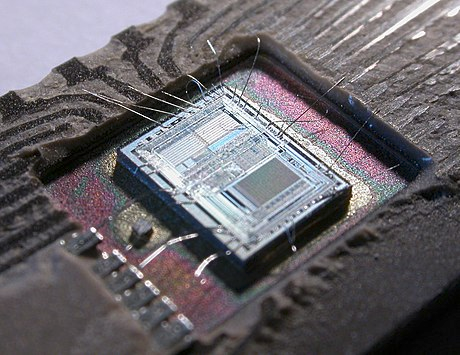
The die from an Intel 8742, an 8-bit microcontroller that includes a CPU running at 12 MHz, 128 bytes of RAM, 2048 bytes of EPROM, and I/O in the same chip https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microcontroller
Knowledge and Skills
- Algorithm development
- Hardware-aware programming, need to know hardware resource implications of code, need to understand hardware to communicate with it
- Computer Organization and Processor Architecture
- Hardware
- Circuits
- Processor-hardware interfaces
- User interfaces (hardware)
- Hardware and Embedded Software Debugging
- Designing embedded systems requires a range of skills from hardware skills to software skills.
- Tools - The diversity of hardware and software components means a verity of development tools are required. We will focus on software tools. The circuit components in this course should be simple enough that hardware design tools are not required.
- Successful system development comes from experience -- knowing options (i.e. top-down design) and where problems will occur (pre-planning for testing).
Design and Development of an embedded system
Creation of a requirements, specifications, and functional description.

- Ideally, the customer provides sufficient specifications, but since often don't understand the implantation's they might have deficiencies in their specifications, including even impossible specifications or ambiguous requirements.
- And experienced engineer can help refine technical requirements and solicit more detail where appropriate.
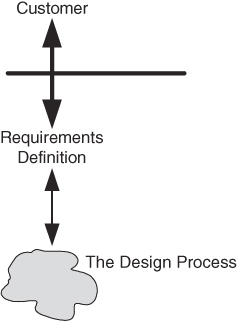
- The engineer must formalize the system and the environment while the customer refines the requirements
- Concentration on formalizing the technical descriptions of the Inputs and Outputs
- A boundary diagram (system context diagram) can help define what the system will do, what it won't do, and what the expected interactions with the environment are
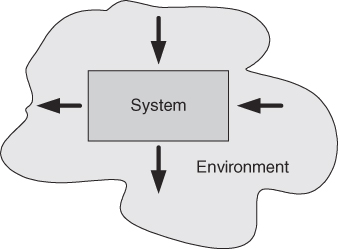
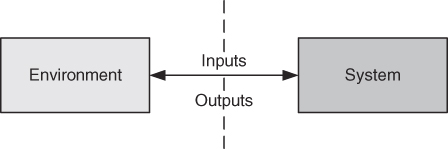
Formalizing the system and engineering teak involves thinking of the system and environment in terms of many processes/tasks with functional descriptions
- Functional Processes and Specifications: Outward looking. Description of what affect on and interaction with the environment is desired.
- Operational Specification: How the system should behave, detailed description of behavior perform by abstracted components, architecture, data flows. Interactions, such as user interactions if required required to achieve the goal, these are captured here.
- Technological Specification: requirements related to the specific solution (e.g. physical and/or software) and how it may be built. Constraints like voltage, allowed software languages, etc.. These details relate to the technology of implementation. For instance a mechanical control system would have different concerns than an electrical control system.
Diagrams
Organization in crucial for engineering of complex systems.
Seek tools, diagraming, and documentation methods that suit the job as well as your personal and team needs.
Several diagram types can be useful for describing requirements and solutions
- activity diagrams: map sequential and concurrent actions
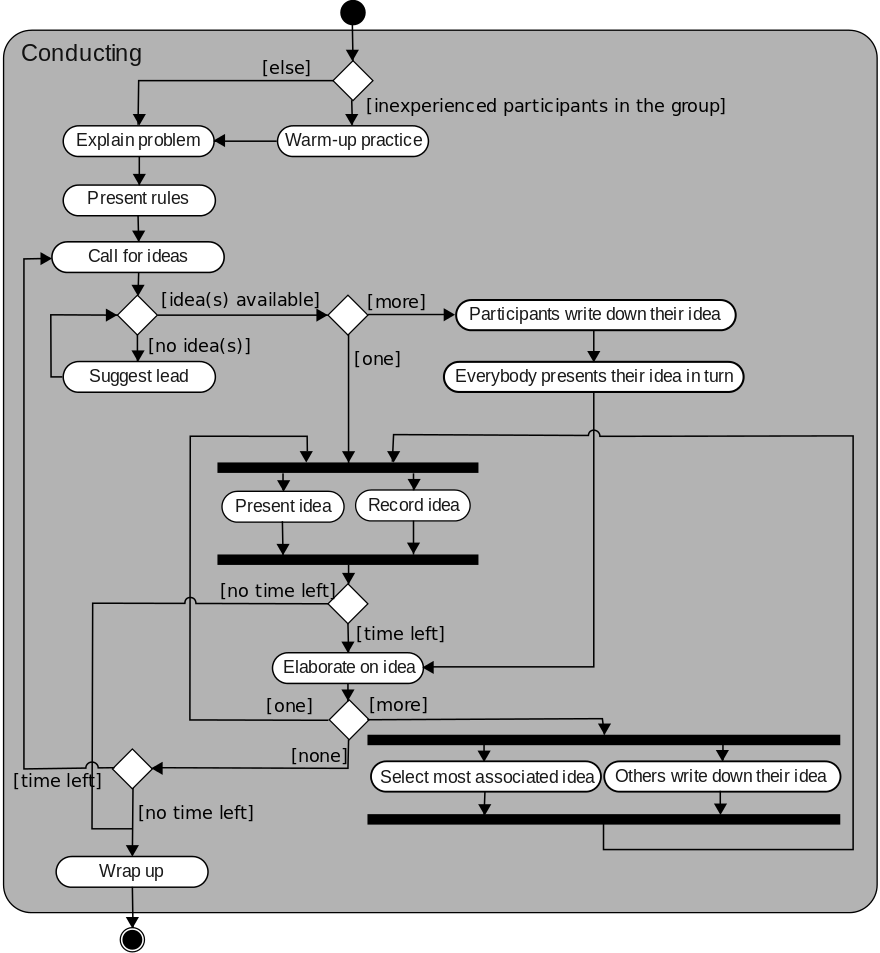 https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Activity_diagram
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Activity_diagram - System sequence diagrams: depict objects involved in tasks and messages exchanged over time to complete a job
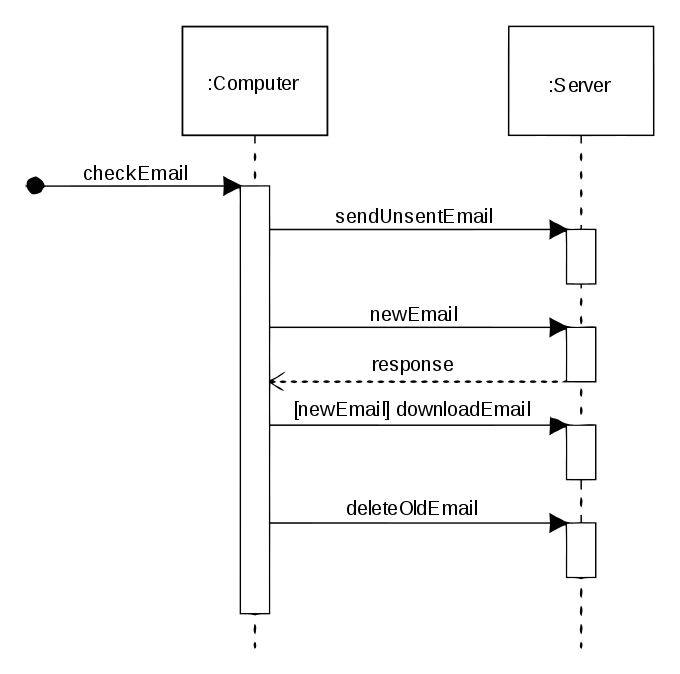 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sequence_diagram
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sequence_diagram - state charts/diagrams (covered extensively in previous course)
- data and control flow diagrams: data flow diagrams depict information transferred between processes/task to complete a job, control flow-diagrams describe the status information, decisions, and actions to that must be triggered trigger
- State diagrams versus control flowcharts:* State diagrams have an emphasis on defining states, and the input events and actions to be performed based on these * Control flowcharts
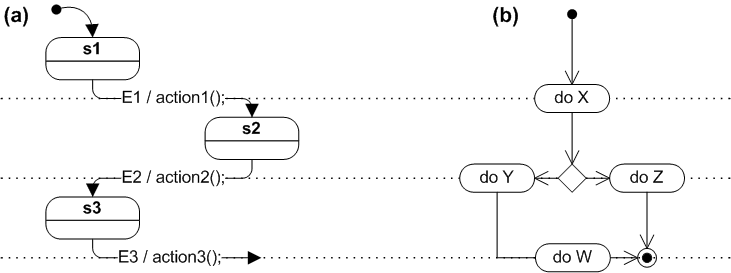 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/State_diagram
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/State_diagram - Dataflow Diagram:
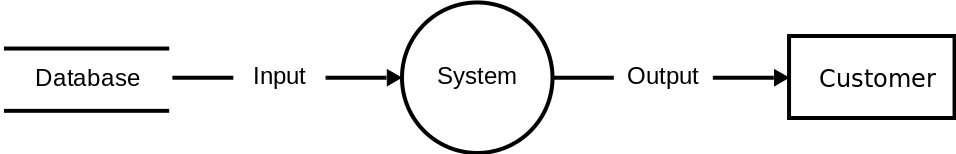 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data-flow_diagram
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data-flow_diagram - Data Flow Graph Commonly used in DSP:
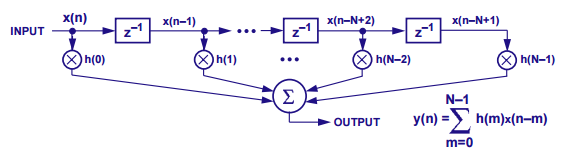 https://www.analog.com/en/analog-dialogue/articles/dsp-101-part-3.html
https://www.analog.com/en/analog-dialogue/articles/dsp-101-part-3.html
- State diagrams versus control flowcharts:
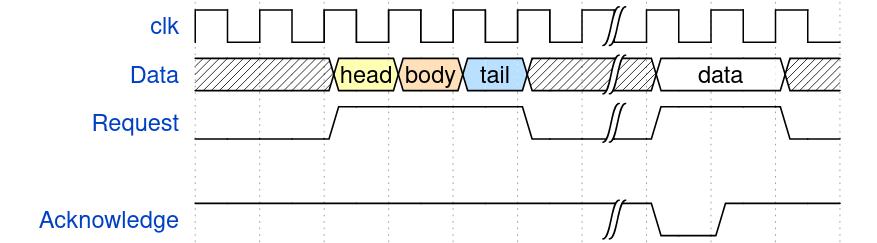
- Timing Diagrams: useful for describing timing specifications and expected sequences of information presented and produced in a system
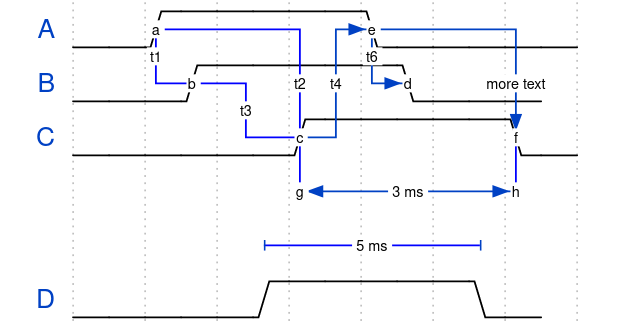 https://wavedrom.com/tutorial.html
https://wavedrom.com/tutorial.html
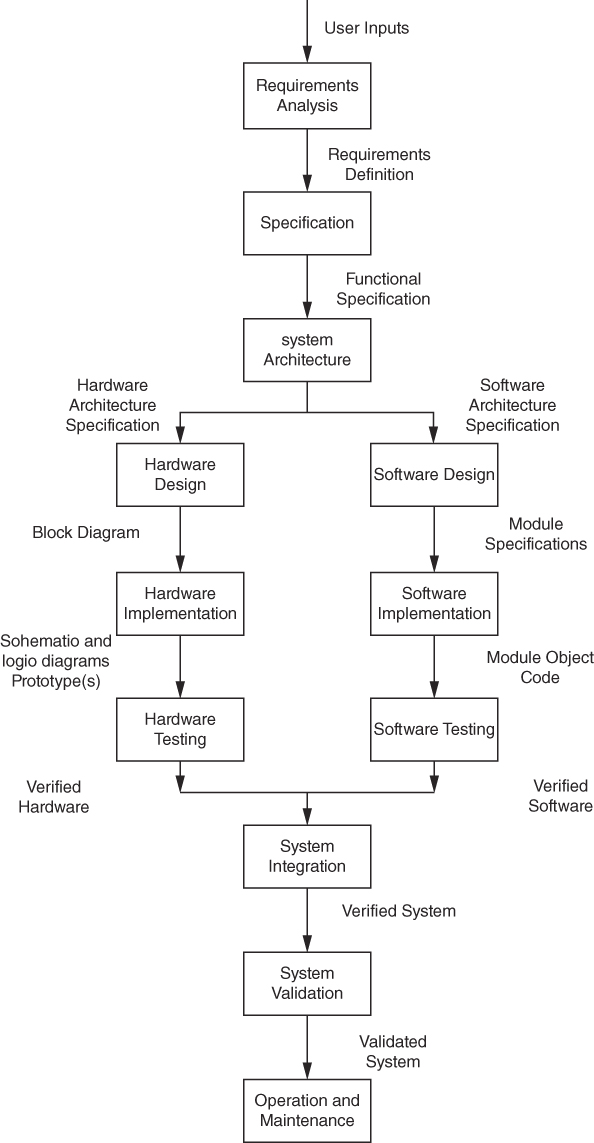
Traditional Design and Hardware/Software Codesign
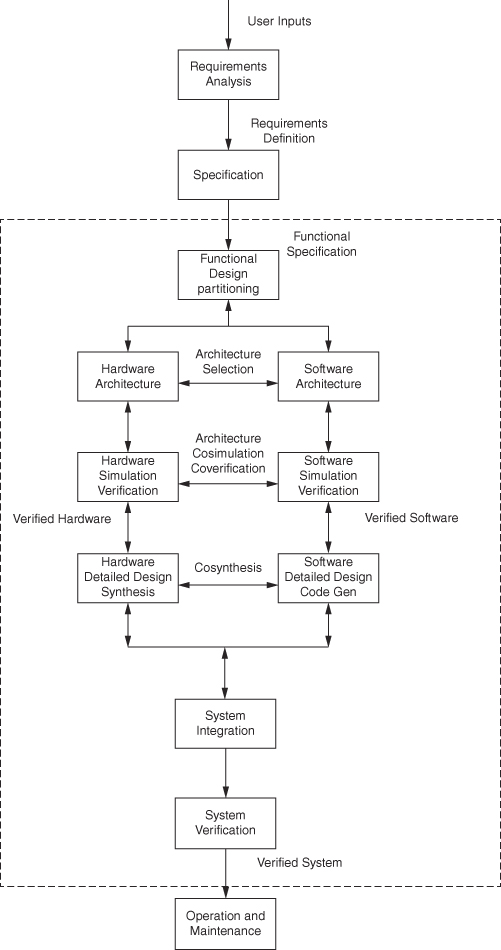
- In the second depiction, the emergent challenge of hardware and software co-design is depicted. It is a complication in design partitioning into specialized engineering efforts.
Design Partitioning and Mapping of Tasks to Technologies
Hardware/Software Partitioning
- Mapping tasks to technological solutions requires diverse knowledge and awareness of the technologies and platform development tools.
- Various tasks may be satisfied by the capabilities of a particular technology
Top-Down Design
top-down design: step-wise refinement, break large problem into smaller problems, subdivide/partition task based on guesses as to what building blocks are realizable and achieable be different design efforts (experience helps immensly here)
bottom-up design: start with something small and achivable, lower risk, and build on top
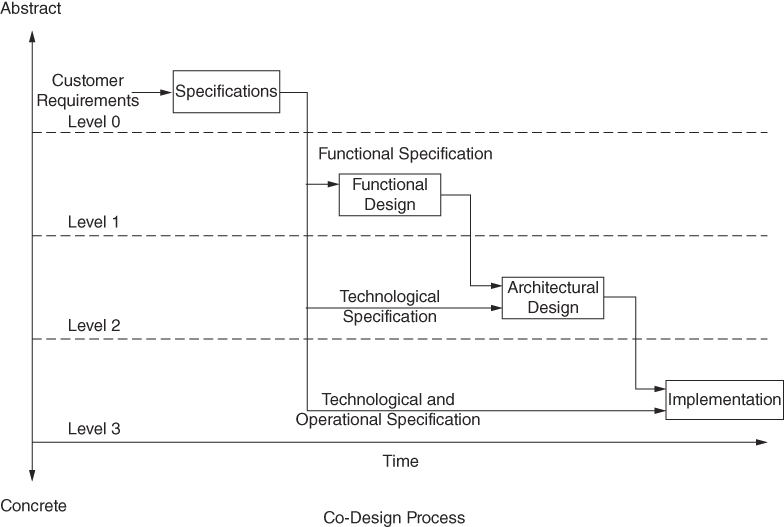
Design Cycles
Waterfall Model
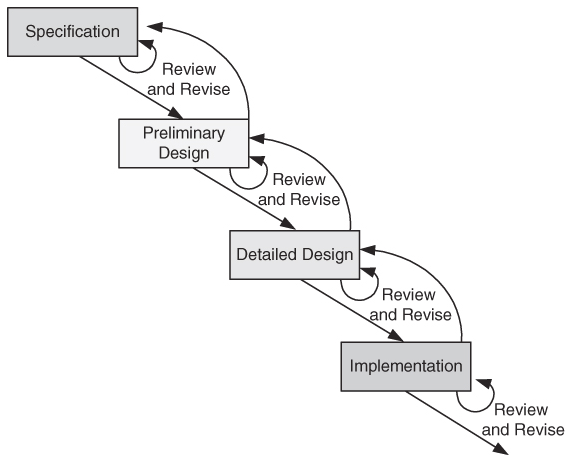
The waterfall model
- Specification
- Preliminary design
- Design review
- Detailed design
- Design review
- Implementation
- Review
The V Cycle Model
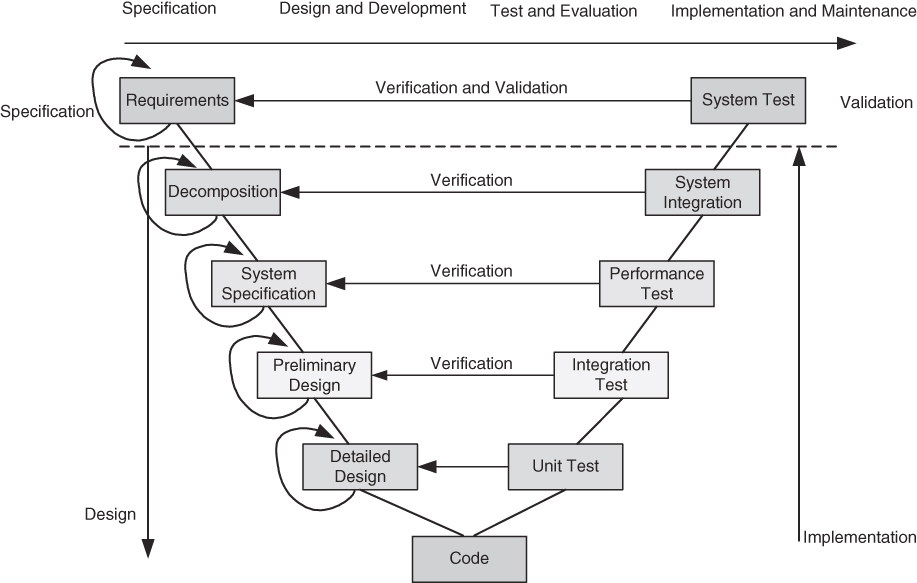
- Note the many design cycles embedded within the graph
- This staged approach is important to consider in design even for this course
The spiral model

The spiral model helps visualize the cyclic nature of engineering, but also captures the possibility of staged releases and product revisions
Additional Ref: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spiral_model
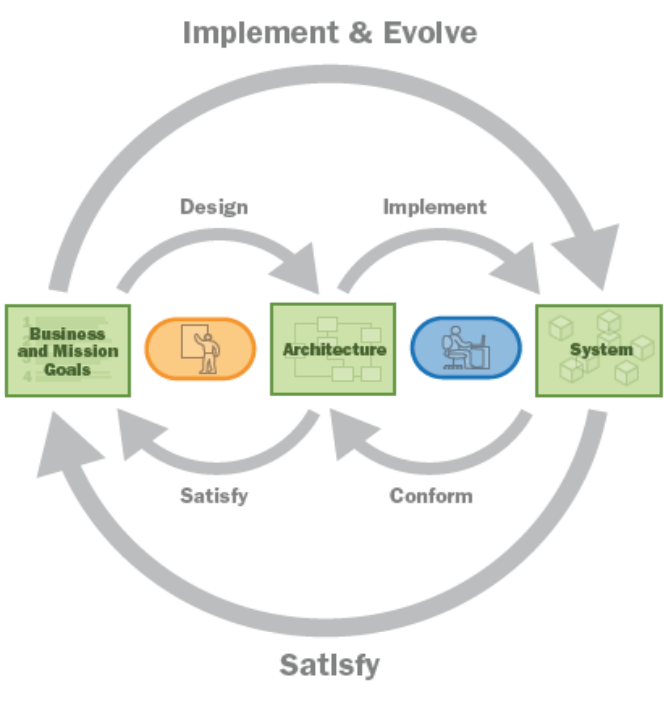
Evolving Systems
A visual depiction of modern software system development:
Syllabus
Course website: https://eclipse.umbc.edu/robucci/cmpe311/
Reading for First Week
Foward and Chapter 1