Lecture 04
Verilog: Case-Statement Based State Machines
Ryan Robucci
• ESC/O-Key to see slide overview • ? to see help
References
Slide Audience
- This presentation includes slides for both a graduate and undergraduate course, but with very different delivery, emphasis, and expectation. The slides marked in title with a superscript circle ∘ are only for the graduate course and should be ignored for the presentation to undergradaute students.
References
-
ꭝꭝ The Verilog® Hardware Description Language, Donald E. Thomas (Author), Philip R. Moorby (Author) ISBN:9781402070891 Amazon Link
- Examples for rescheduling
Finite State Machine (FSM)
- Characterized by
- A set of states
- A set of inputs and outputs
- A state transition function
- An output function
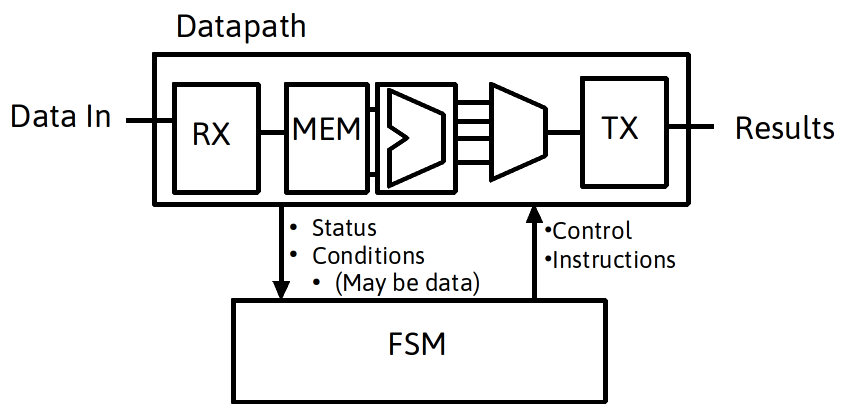
Finite State Machine with Datapath
- A very common framework being described and implemented is a Finite State Machine with a Datapath: a data path controlled by signals from a FSM
Books FSM Hardware Implementation
- suitable for implementation of algorithm with input and local variables stored in datapath register
- Hardware Implementation:
- Current State held in a register
- Any additional status information held in status register
- Next-State and State Control Logic Determines next state and control signals based on registers
- Datapath implements operations on data under control of sate control logic
Components of a modeling/description language for FSM ∘
-
- Wires and registers with specified precision and sign
- Arithmetic and bitwise operations
- Comparison Operations
- Bitvector Operations (selecting multiple bits from a vector)
- Selection
- Indexed Storage
- Organization and Precedence
- Modules (Hardware)
Software and Hardware ∘
- If available customizable hardware is fast, and control logic is difficult to describe, a good mix can be software for control and hardware for calculations. We will see later approaches that use a general purpose processor for control.
4 Rules of Proper FSMD ∘
- The relate to describing a piece of hardware (or software) in a modeling language which is software.
- 1 Neither registers nor signals can be assigned more than once during a clock cycle (covered in our Verilog code rules by the one-block assignment rule)
- 2 No circular definitions exist between wires (i.e. no combinatorial logic loops)
- 3 If a signal is used as an operand of an expression, it must have a known value in the same clock cycle
- 4 All datapath outputs must be defined (assigned) during all clock cycles (in some cases a DontCare may be allowed)
Hardware/Software Partitioning ∘
- For a general application, hardware is best for timing-critical (especially simultaneous processes and triggering events) while software is flexible and good for implementing algorithms with high complexity – in the sense of Kolmogorov complexity, the length of the code to implement the algorithm to produce some output given some inputs.
- Remember, timing-critical can refer to predictability of timing, not just how fast it can go (a real-time system is a system with timing guarantees)
Control and Datapath Partitioning
- Datapath operations can be encoded in the state machine description or can be build separately.
- If pre-built modules are used, as is common, the datapath is necessarily a separate description.
- Often the datapath represents the algorithm calculations, separating the datapath code makes the code more readable
- Coding datapath separately can allow more explicit influence over and insight into the resources used for computation while separating details of control code
- Can sometimes think of datapath as implementing instructions for the controller to invoke/call
- Separating the datapath code can allow better reuse under a different scheduling of operations (implementing a different algorithm)
- In general, designing the datapath first and then the control is a good strategy
Temporal Processes of statemachine
 ꭝ
ꭝ
- Just after clock edge, state variables are updated. For controller this means that a state-transition is complete and state registers holds the new current state. For the data path, this means that the register variables are updated as a result of assigning (algebraic, boolean, logical, etc...) expressions to them.
- Controller FSM Combines the control state and the data-path state to evaluate the new next state for the, at the same time it will also select what instructions should be executed by the datapath
- The datapath FSM will evaluate the next-state for the state variables in the datapath, using the updated datapath state as well as the instructions received from the control FSM
- Just before the next clock edge, both the control FSM and the datapath FSM have evaluated and prepared the next-state value for the control state as well as the datapath state
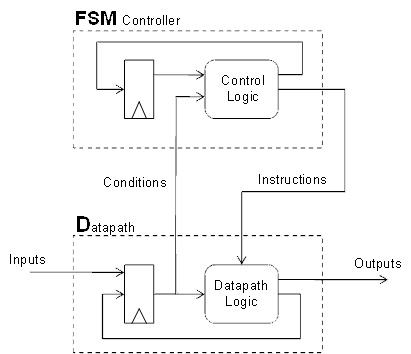
Controller FSM vs Datapath
-
Controller FSM
- IrregularStructure
- Very well-suited for FSM-style description, difficult to describe with (boolean) expression-based
- Registers represent the familiar sense of the state of the system
-
Datapath
- Regular Structure
- Often easy to describe with expressions or structurally build with blocks
- Registers represent algorithmic states (intermediate or partial results)
Divide and Conquer
-
Datapath operations can be encoded within the same procedural code as the state machine description or can be built separately.
-
First consider partitioning.
- Identify elements in the datapath from experience with traditional digital systems (e.g. communications modules, arithmetic modules, multiplexer's and demultiplexers, registers and multi-word buffers, FIFOs, IP Cores etc…).
- Identify the control signals required and the status/condition information required to make decisions on the control.
State Machine with High Branching and Merging
-
example find borg|car|cat|bat|bot|bet|bit and output done flag where done is a registered output
-
done flag logic cannot be coded directly based on CS and with the final states
-
registered outputs in general must coded once per transistion, though the existance of one common default may save some lines of code
always @ (posedge clk) begin CS<=failed; //defaults found<=0; done<=0; //defaults case (CS) ... recieved_a: if (input =='r') begin CS<=recieved_r_for_car; done<=1; found<=1; end else if (input =='t') begin CS<=recieved_t; done<=1; found<=1; end else begin CS<=failed; //covered by default done<=1; found<=0; end ...
-
output logic coded with use of next state NS
CS<=failed; found<=0; done<=0; //defaults case (NS) recieved_t:done<=1;found<=1; recieved_r_for_car:done<=1;found<=1; recieved_g:done<=1;found<=1; failed:done<=1;found<=0; default:done<=0; ...
Algorithmic Statemachines

- However, encoding datapath operations WITHIN in the statemachine description with the controller instead of coding them in a separate block is sometimes better.
- It is common to see "algorithmic" statemachines described with control and computation embedded in the same procedural block. These are modules which perform complex computations over multiple cycles and require internal registers/memory.
- We’ll first focus on control state machines first, with an emphasis on timing and external status and control signals then discuss computational statemachines
Data-Flow Graph
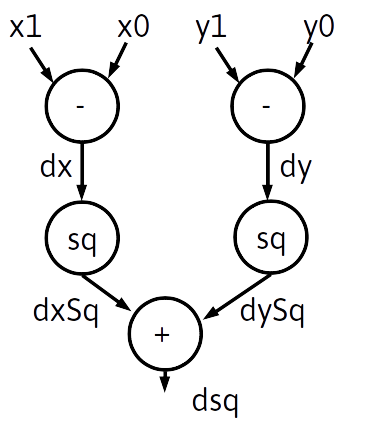
- Data-Flow Graphs represents dependencies among operations in the process of an arithmetic algorithm (more compact than a full state diagram).
- A algorithmic state machine performs one or more operations in a state (i.e. clock cycle) while satisfying the required order dependencies from the graph
- Ex: Draw the Datapath and Identify Status and Control as well as Pre-Register data names

case(CS) S0:begin dx <= x1-x0; busy<= 1; end S1:dx <= y1-y0; S2:dxSq <= dx*dx; S3:dySq <= dy*dy; S4:begin dsq <= dxSq+dySq; busy<= 0; end endcase
Extended State Registers
-
At times we’ll want to include an extra register to store information that we don’t want to code as part of our primary state register.
- Examples:
- partial results in the process of a multi-cycle computation
- saved results to provide at the output ports at a later time
- status flags for events that should be remembered and used in later processing and state decisions
- event counters
- timing counters, to control timing without creating additional states
- Examples:
-
These extended state registers are not necessarily represented by the number of drawn states state transition diagram or the primary coded state register, but formally they ARE part of the state of the system
note the explicit state register and the additional extended state registers
Control FSM Cycle Timing
- Control FSM are commonly required to implement timing based on cycles, reading of status signals in particular cycles, and generating control signals at the appropriate time
Waiting – Conditional and Unconditional
- It is common to require one or both of
- conditional waiting
- unconditional waiting
- These can be used to implement
- Fixed waiting – unconditionally wait a predetermined number of cycles
- Minimum wait (Fixed+Conditional)
- fix delay then wait for a condition based on external input to be satisfied. This is useful when interfacing with external “slow” entities that need time after being signaled to send back a response.
Implementation of Waits
Some Options:
- Add “top” level wait states to state machine in each place needed
- Use a counter
- a) Use external counter ( implement as an external state machine) and interface to it
- b) embed something like a counter in the coding of the state machine, thus creating substates using the counter as an extended state register.
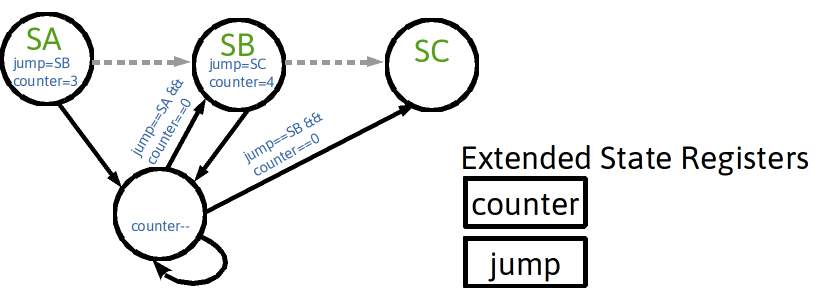
- Create a single programmable wait state to jump to and return to from multiple states using a “jump” register extended state register
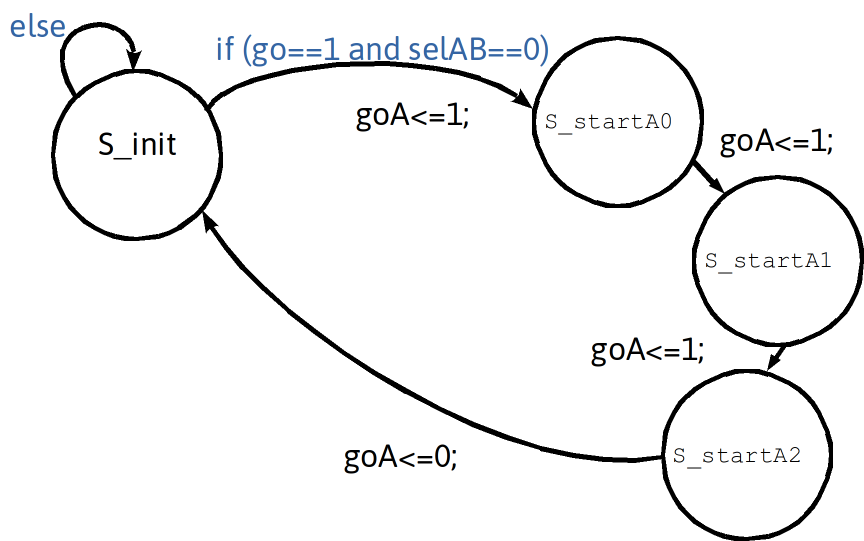
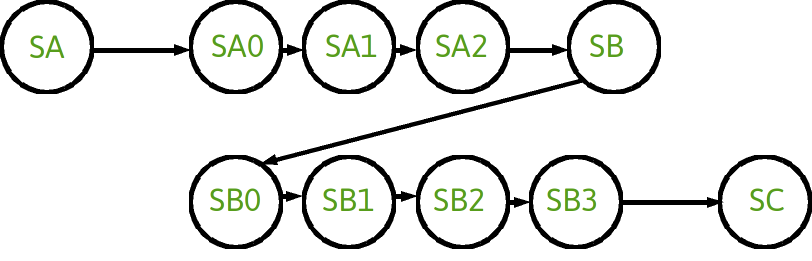
Unconditional Delay Using Extra States
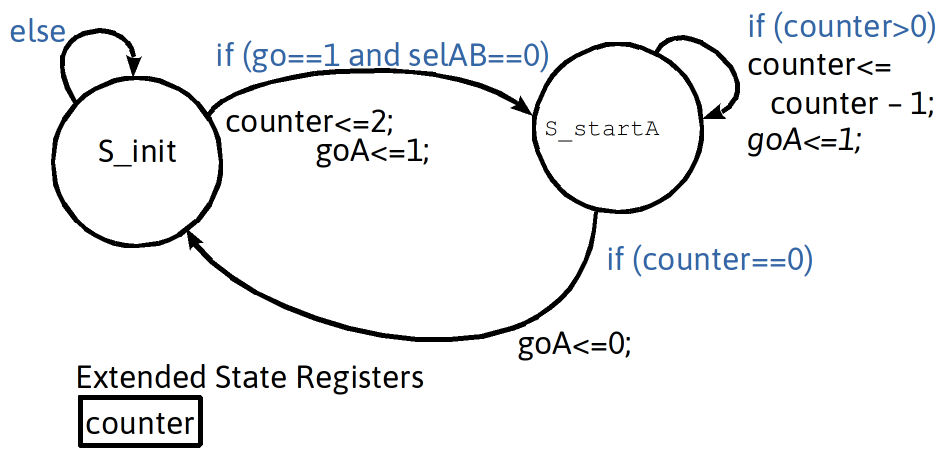
Unconditional Delay Using Extended State Register Variable : Counter
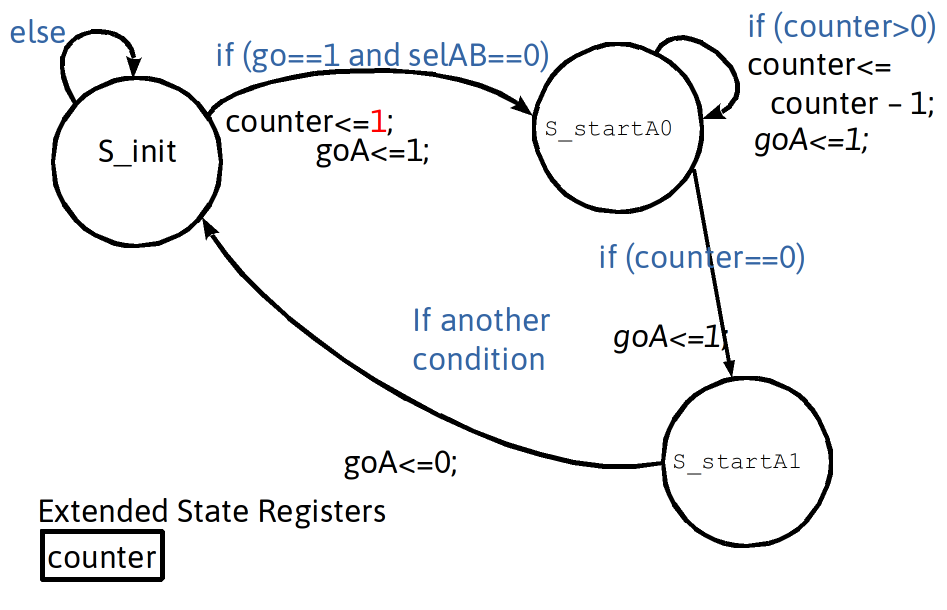
Minimal Pause: Delay + Conditional Exit Using An Extra State (unconditional delay +conditional exit)
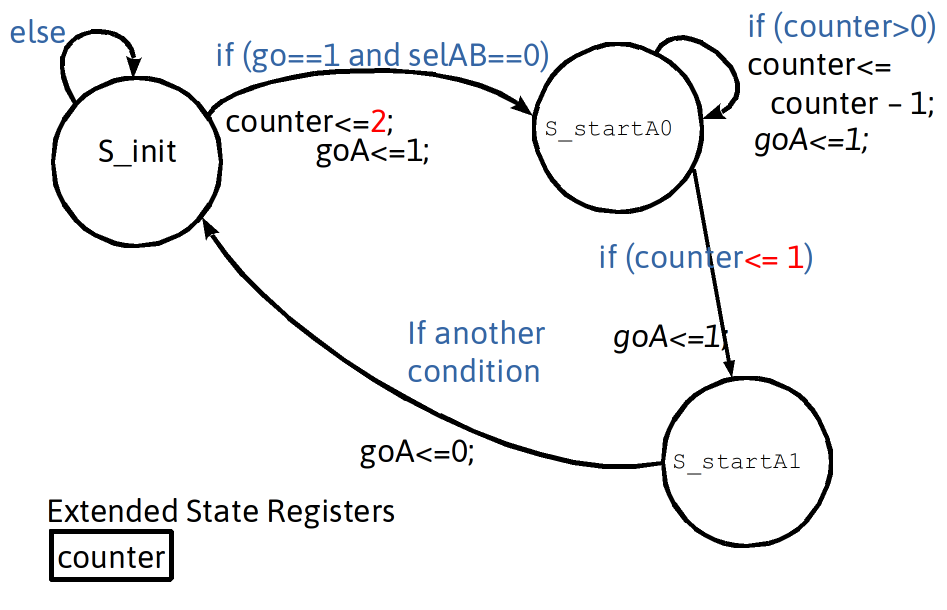
Minimum Wait: Delay + Conditional Exit Using Extended State Register Variable Counter
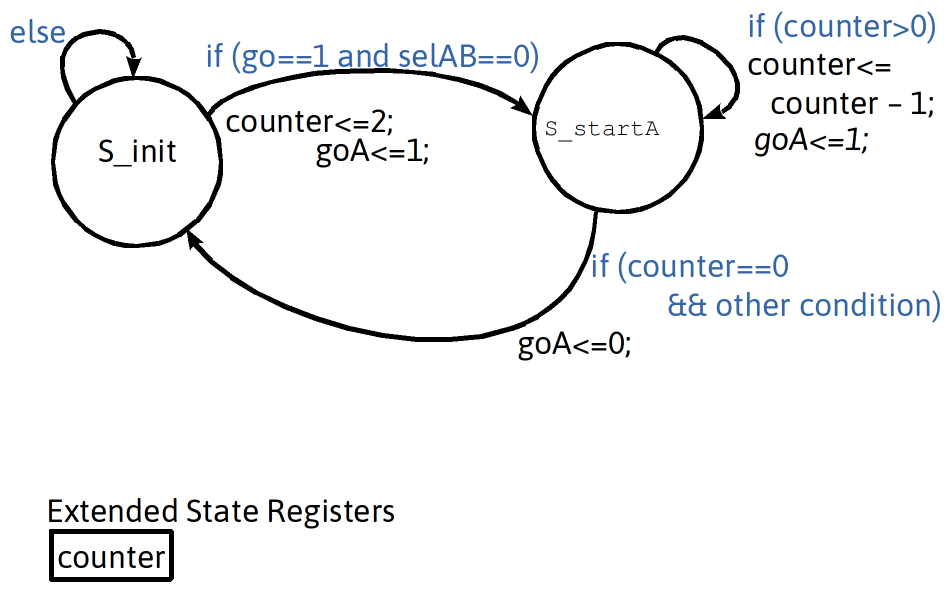
Programmable Wait State
- Explicit Top-Level States vs Programmable State
- Explicit
- Programmable
- Explicit
Thought Question
- Is it better to grow the state register or use a separate counter variable?
- no simple universal answer
“For Loop” State Machine
- Extended-state registers can help implement loop behaviors
- Example: create outer loop with 10 iterations and inner loop with 5 iterations
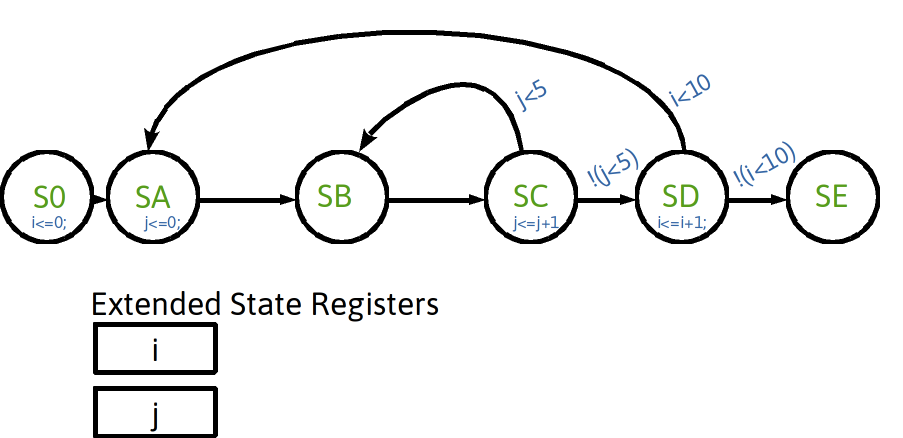
Drawing Possible Hardware
Realizations of i,j registers and support hardware
- After examination of the state diagram, three required behaviors are desired: Hold, Increment , Load 0
- A primary FSM will generate the control signals
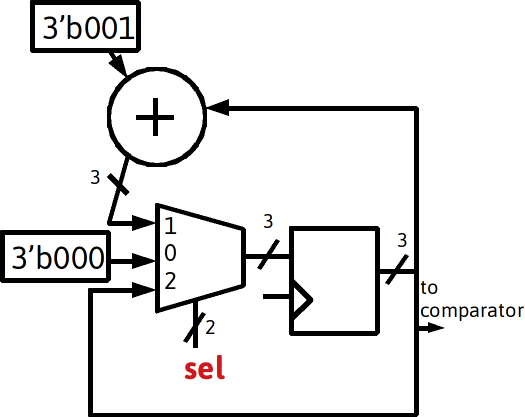
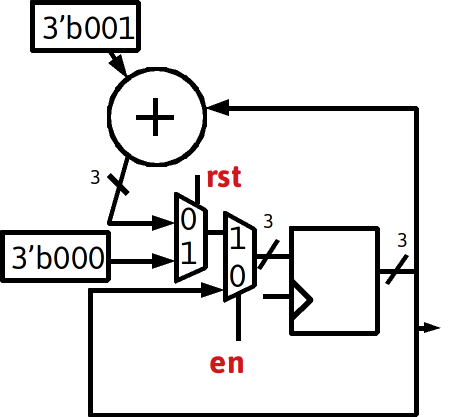
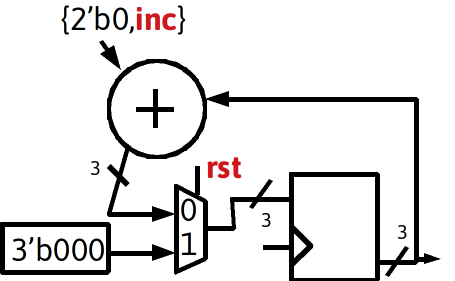
- Note i would be the output of the register, the output from the register could be called (i_next , _i, i_comb, i_int, i_prereg)
class discussion: timing diagram
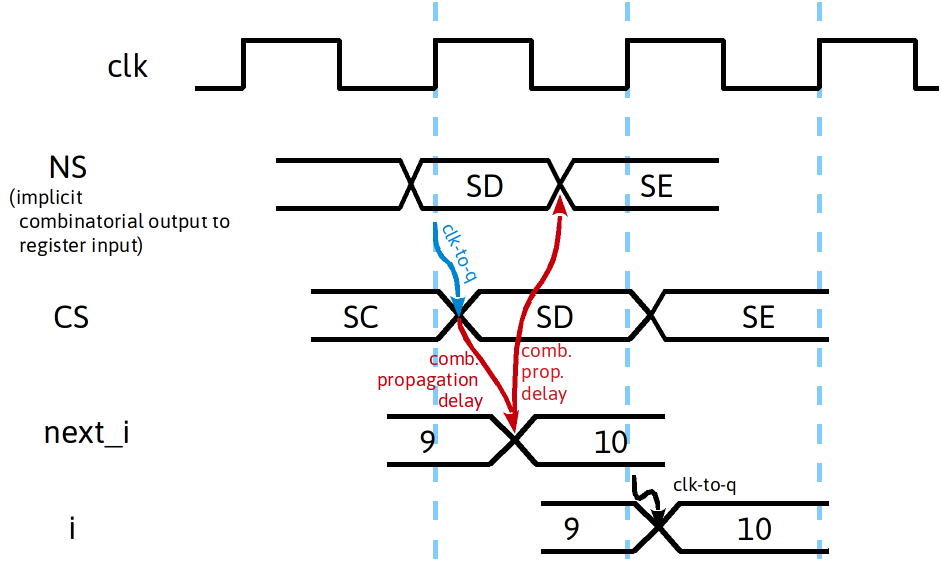
Combinatorial vs Sequential Pitfalls
- Wrongly using the output of a register instead of the input can be a pitfall when using single-always-block (registered outputs) and extended state registers
Wrong Code State D
SA: i<=0; ... SD: i <= i+1; if (i<10) CS<=SA; else CS<=SE; ….
Correct Code State D
SD: next_i = i+1; if (next_i<10) CS<=SA; else CS<=SE; i <= next_i; ….
Tweaking Question ( a question asked in class)
- Could one just change i<10 to i<9?
Wrong Code State D
SA: i<=0; ... SD: i <= i+1; if (i<10) CS<=SA; else CS<=SE; ….
Tweaked / “Hacked”
SA: i<=0; ... SD: i <= i+1; if (i<9) CS<=SA; else CS<=SE; ….
- Perhaps yes, but the reasoning is important.
- Lets say you are working on a class HW project – if you make the wrong version, run a simulation or debug in FPGA hardware, notice that one extra loop is performed and “tweak” the code to “just make it work” without understand the options, than that would not be a good reason. You want to be cognizant of and understand the different choices, then you have the knowledge and understanding to select the most appropriate implementation. Furthermore, at some point your code will be very large and systems will be complex – expecting to make many tweaks is not a reliable approach. You want to learn to get as much right the first time as possible.
- I'd argue that the tweaked version is less readable, but I could not say it is wrong.
Detecting Signal Change in Single-Clock-Domain Synchronous Logic
-
When looking for a change on an signal, avoid a careless temptation to “detect” edges using edge specifiers if it is not warranted to create a new clock domain. Ex:
always @ (posedge e) e_counter <= e_counter + 1;
-
Consider saving a previous version of the signal in a register, and using both present and previous input values to detect a transition:
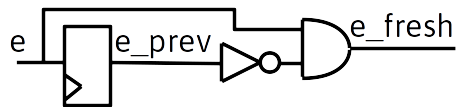
always @ (posedge clk) begin if (~e_prev & e) e_counter <= e_counter + 1; e_prev<=e; end
which is the same as
always @ (posedge clk)begin e_prev<=e; if (~e_prev & e) e_counter <= e_counter + 1; end
One Reaction per Transition
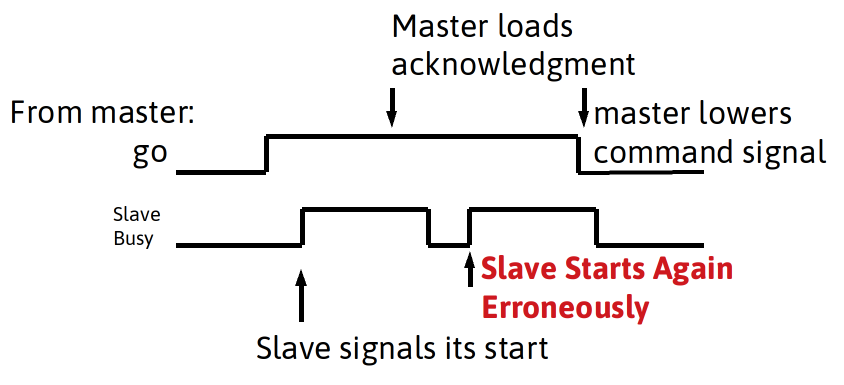
- A slave device commonly starts processes based on a start signal from a master. A slave process may be fast or slow compared to a master. For instance, an instruction processor acting as a master controlling a slave through general I/O ports. Driven by software, it the processor may require many clock cycles to respond (software bit-banging and handshaking can be slow).
- Considering a slow master applying a command signal, yet requiring many clock cycles to respond to a handshaking signal from a slave. The slave might falsely initiate a second round of activity if the command is asserted too long.
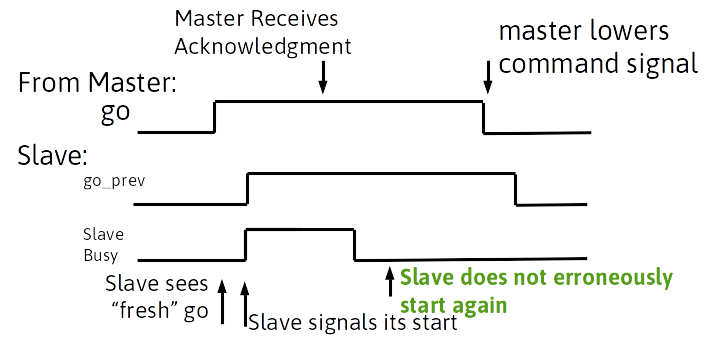
Transition detection for statemachines
-
To alter the behavior, a slave state machine can instead look for a change in the signal in two consecutive clock cycles
-
Saving the previous input value:
always @ (posedge clk) go_prev<=go;
-
using a fresh high as a condition
(go==1 && go_prev==0)
Limitations of FSM
- FSM typically lack any hierarchy. There is no way to connect details of state-machines leading to state explosion. Otherwise, a hierarchy of states is quite useful for organizing an algorithm.
State Machine State Explosion
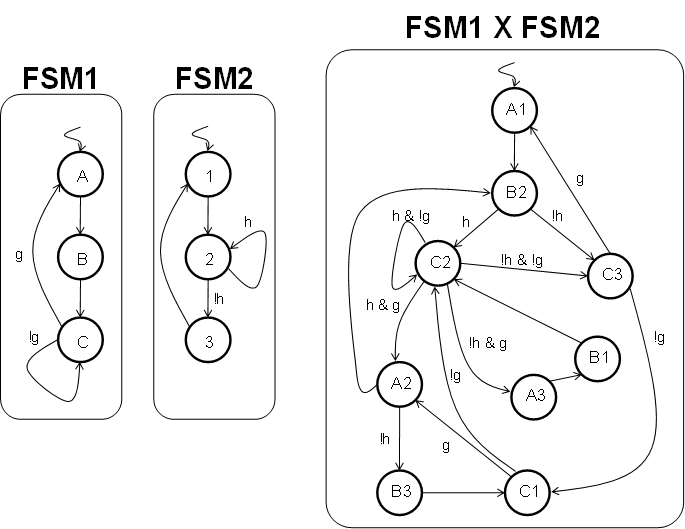
- Consider two state machines. Maybe one captures user input like desired temperature, it has states, inputs and outputs appropriate to perform that task. Perhaps the other controls a heating element based on measured and desired temperature. Separated, they may be fairly simple, but what happens when they are described as a single, flat state machine?
- A multiplicative effect in the number of states. Two three-state FSMs became one nine-state FSM
- This motivates partitioning into multiple state machines in hardware design
Global Exceptions
- Now, see what happens if a single new condition, a universal exception must be added.
- A dramatic result from only one new condition. Readability and perhaps feasibility of mentally managing the FSM is severely impacted.
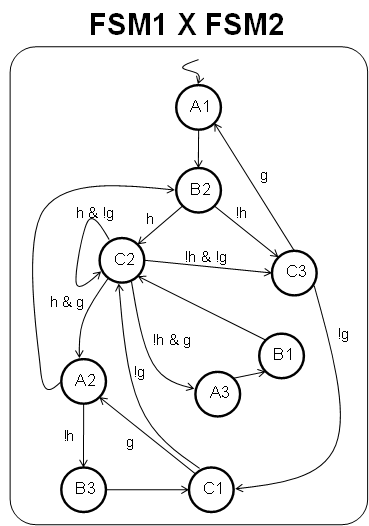
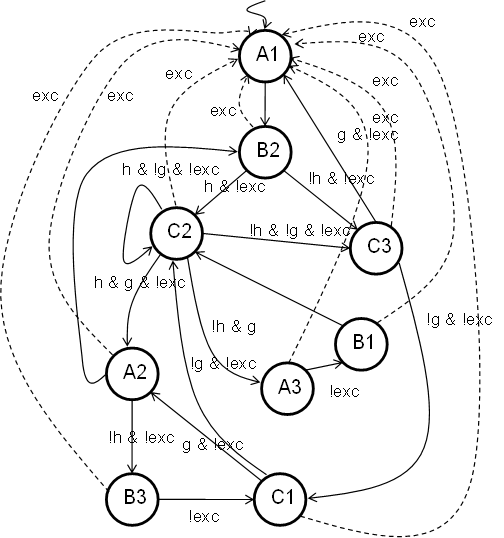
Global exception in software
- A single if statement can be added, taking advantage of the hierarchy of logic embedded in code.
switch(current_state){ case A: … case B: … case C: … case D: … }
if (exception){ do this }else{ switch(current_state){ case A: … case B: case C: case D: }
Delay/Pause/Waiting
- Think about the delay examples given earlier using a counter. The counter was implementing one form of hierarchical states.
- Consider waiting for an acknowledgment signal for 220 clock cycles. This would require ~1 Millon states with the condition to move to the next state or proceed to end state if acknowledge was received.
Runtime Flexibility ∘
- The rigid implementation of hardware and the limited representation of FSMs do not make it very flexible model, especially if one considers run-time flexibility
Microprogrammed Control ∘
- Rigid next-state logic is replaced by a rigid next-address logic with a programmable control store.
- Complex designs make require using/creating some form of compiler and a custom language
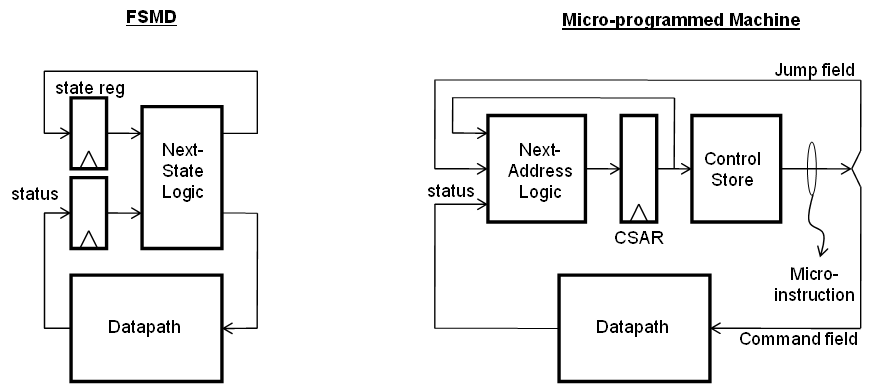
General Processor Control ∘
- Next step towards generalization is to use a general purpose processor
- A number of models exist for doing that, from implementing custom hardware as a slave coprocessor that implements hardware-accelerated instructions (or functions) to treating the custom hardware modules and processor as cooperative peer components.
- Interfacing is another issue and choices depend on rigidness of interfaces and which should be the master or slave.
- Common choices:
- Confirm hardware design to be able attach to processor bus
- Write a hardware wrapper to attach hardware to system bus
- Use general IO to interface processor to hardware
- With respect to the processor, need to decide on interrupt or polling interface. Platforms should provide options for both for all the choices above
- Common choices:
Multi-Cycle Computations as FSMs
- In the following slides, we will consider examples of algorithmic FSMs. These are used to describe and synthesize multi-cycle computations. The number of state transitions defined are typically less than with a complex controller FSM.
- A more regular, forward, orderly progression through the states is typical, and the designer’s thought processes may be focused on the computation being performed in each state and the resulting partial results (in registers), as opposed to the output during the state.
- Thus, it becomes more reasonable to use a single edge-triggered always block in the design. The fewer number of transition decisions (branches) makes the concern of code bloat negligible.
FSM Optimizations
- As we are designing Multi-Cycle computations, we may consider two
optimizations:- Rescheduling – moving internal operations to other states
- Resource sharing – utilizing same component in multiple states
- The following examples based on or borrowed from ꭝꭝ Thomas&Moorby
Module Header
module FSM_opt( output reg [7:0] f, input clk, input wire [7:0] i, input wire [7:0] j, input wire [7:0] k, input rst ); reg [7:0] CS; reg [7:0] i_int,j_int,k_int; localparam S_0 = 8'b00000000; localparam S_1 = 8'b00000001; localparam S_2 = 8'b00000010;
Module Body
always @ (posedge clk) begin if (rst) begin CS<=S_0; f<=0; end else begin case(CS) S_0: begin i_int<=i; j_int<=j; k_int<=k; CS<=S_1; end S_1: begin CS<=S_2; end S_2: begin m=i_int*j_int; f<=m*k_int; CS<=S_0; end endcase end end endmodule
- Multi-cycle computation:
Note, the single-block style here was used since the state transition sequence is straightforward. Also, the data path is combined with the controller.
We are not worried about “code bloat” from having to code each output on every transition.
Instead of concentrating on
timing coincidence of state and outputs
vs
coding coincidence of state and outputs,
we are focused on the
coincidence of states and computations. In this single block style the computation performed and resources required for each each are clear, though the corresponding output of each computation is seen and can be used on the cycle following the corresponding state indicated in the state register.
RTL suggested from Code
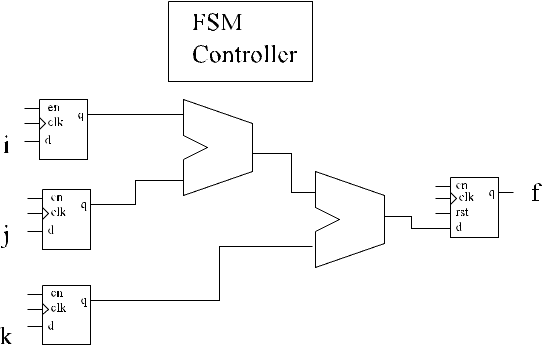
Only datapath connections shown, control and status signals are ommitted
Alternative RTL supporting higher clk rate

Rescheduling
always @ (posedge clk) begin if (rst) begin CS<=S_0; f<=0; end else begin case(CS) S_0: begin i_int<=i; j_int<=j; k_int<=k; CS<=S_1; end S_1: begin m<=i_int*j_int; //**to here** CS<=S_2; end S_2: begin //m=i_int*j_int; //**move from here** f<=m\*k_int; CS<=S_0; end endcase end end endmodule
Rescheduling this multiply allows for faster clock rates ( assuming two clock cycles were required at the system level). Some synthesizers may do similar types of rescheduling for you.
Reference Computation Module for discussion
Head
module FSM_opt( output reg [7:0] f, output reg [7:0] g, input clk, input wire [7:0] i, input wire [7:0] j, input wire [7:0] k, input rst ); reg [7:0] CS; reg [7:0] i_int,j_int,k_int; localparam S_0 = 8'b00000000; localparam S_1 = 8'b00000001; localparam S_2 = 8'b00000010;
Body
always @ (posedge clk) begin if (rst) begin CS<=S_0; f<=0; h<=0; end else begin case(CS) S_0: begin i_int<=i; j_int<=j; k_int<=k; CS<=S_1; end S_1: begin CS<=S_2; end S_2: begin f<=i_int*j_int; h<=j_int*k_int; CS<=S_0; end endcase end end endmodule

Alternative RTL with lower gate count
always @ (posedge clk) begin if (rst) begin f<=0; g<=0; CS<=S_0; end else begin case(CS) S_0: begin i_int<=i; j_int<=j; k_int<=k; CS<=S_1; end S_1: begin CS<=S_2; end S_2: begin f<=i_int*j_int; //** g<=j_int*k_int; CS<=S_0; end endcase end end endmodule
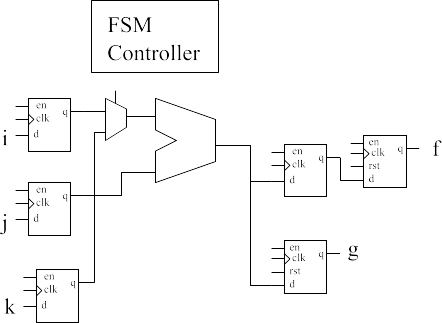
Explicitly coding the rescheduling so that only one multiply is performed per cycle is simple and seen in the next code. However, this doesn’t ensure resource sharing as shown in the figure with one a single multiplier.
Alt. Module Body
always @ (posedge clk) begin if (rst) begin f<=0; g<=0; CS<=S_0; end else begin case(CS) S_0: begin i_int<=i; j_int<=j; k_int<=k; CS<=S_1; end S_1: begin f_int<=i_int*j_int; //**moved to here**// CS<=S_2; end S_2: begin f<=f_int; //*timed output load*// g<=k_int*j_int; CS<=S_0; end endcase end end endmodule
Resource Sharing
- Suggesting Resource Sharing guides the synthesizer to reuse hardware for operations at multiple places in the code
- The coding method depends on the synthesizer tool: the following code is more likely interpreted as resource sharing since the multiplier result is always written to the same variable
always @ (posedge clk) begin:named reg [15:0] mult_out; mult_out = 16'bx; if (rst) begin f<=0; g<=0; CS<=S_0; end else begin case(CS) S_0: begin i_int<=i; j_int<=j; k_int<=k; CS<=S_1; end S_1: begin mult_out=i_int*j_intl; //** f_int<=mult_out; //** CS<=S_2; end S_2: begin f<=f_int; mult_out=k_int*j_int; //** g<=mult_out; //** CS<=S_0; end endcase end end endmodule
- Another option is to pull the multiplier out of the edge-triggered code and write logic explicitly for the multiplier, and use the state machine to change the inputs to the multiplier
Another Rescheduling Example
Version 1
… always @ (posedge clk) … case (CS) S_0:begin q<=r+s; CS<=S_1; end S_1:begin CS<=S_2; end S_2:begin qout<=q+5; CS<=S_0; end …
Version 2
… always @ (posedge clk) … case (CS) S_0:begin q<=r+s; CS<=S_1; end S_1:begin q<=q+5; CS<=S_2; end S_2:begin qout<=q; CS<=S_0; end …
Yet Another Rescheduling Example
Code Provided to the Synthesizer
input [7:0] i,j,k; output [7:0] f,h; reg [7:0] f,g,h,q,r,s; always @ (posedge clk) … case (CS) S_0:begin[ f<=i+j; g<=j*23; CS<=S_1; end S_1:begin[ h<=f+k; CS<=S_2; end S_2:begin[ f<=f*g; q<=r*s; CS<=S_0; end …
- FSM Synthesizers can automatically try variations:
-
Movement of q=r*s using a temporary variable:
S_0:begin[ f<=i+j; g<=j*23; CS<=S_1; end S_1:begin[ h<=f+k; q_int<=r*s; CS<=S_2; end S_2:begin[ f<=f*g; q<=q_int; CS<=S_0; end
-
Movement of f*g:
S_0:begin[ f<=i+j;g<=j*23; CS<=S_1; end S_1:begin[ h<=f+k;g<=f*g; CS<=S_2; end S_2:begin[ f<=g; q<=r*s; CS<=S_0; end
-
State Encoding
- The state encoding effects the size of the decoder, speed, dependent logic optimization, etc.
- Encodings supported by Xilinx: http://www.xilinx.com/support/documentation/sw_manuals/xilinx11/xst.pdf
- Auto
- One-Hot
- Gray
- Compact
- Johnson
- Sequential
- User
- Speed1
- RAM-based
State Encodings
- Auto: In this mode, XST tries to select the best suited encoding algorithm for each FSM.
- One-Hot: One-hot encoding is the default encoding scheme. Its principle is to associate one code bit and also one flip-flop to each state. At a given clock cycle during operation, one and only one bit of the state variable is asserted. Only two bits toggle during a transition between two states. One-hot encoding is very appropriate with most FPGA targets where a large number of flip-flops are available. It is also a good alternative when trying to optimize speed or to reduce power dissipation.
- Gray: Gray encoding guarantees that only one bit switches between two consecutive states. It is appropriate for controllers exhibiting long paths without branching. In addition, this coding technique minimizes hazards and glitches. Very good results can be obtained when implementing the state register with T flip-flops.
- Compact: Compact encoding consists of minimizing the number of bits in the state variables and flip-flops. This technique is based on hypercube immersion. Compact encoding is appropriate when trying to optimize area.
- Johnson: Like Gray, Johnson encoding shows benefits with state machines containing long paths with no branching.
- Sequential: Sequential encoding consists of identifying long paths and applying successive radix two codes to the states on these paths. Next state equations are minimized.
- Speed1: Speed1 encoding is oriented for speed optimization. The number of bits for a state register depends on the particular FSM, but generally it is greater than the number of FSM states.
- User: In this mode, XST uses original encoding, specified in the HDL file. For example, if you use enumerated types for a state register, then in addition you can use the ENUM_ENCODING constraint to assign a specific binary value to each state. Please refer to "Design Constraints" chapter for more details.
- RAM-Based Finite State Machine (FSM) Synthesis: Large Finite State Machine (FSM) components can be made more compact and faster by implementing them in the block RAM resources provided in Virtex® devices and later technologies. FSM Style (FSM_STYLE) directs XST to use block RAM resources for FSMs.
Unreachable States
- One of the benefits of extracting FSMs, is that additional analysis and design checks are available:
"XST can detect unreachable states in an FSM. It lists them in the log file in the HDL Synthesis step."
Safe Finite State Machine (FSM) Implementation
- XST can add logic to your Finite State Machine (FSM) implementation that will let your state machine recover from an invalid state. If during its execution, a state machine enters an invalid state, the logic added by XST will bring it back to a known state, called a recovery state. This is known as Safe Implementation mode.
- By default, XST automatically selects a reset state as the recovery state. …
- This feature is useful in system susceptible to corruption or as a way to handle undefined power-on initialization
Encoding Review
- One-hot encoding is good for speed and simplicity of state decoding logic and state incrementing.
- More compact codes such as standard binary encoding generally require a smaller state state register than one-hot encoding at the possible cost of size and speed.
- But this depends on the density of combinatorial logic vs. registers the supporting HW platform and in the design.
- FPGAs have many registers and so the cost of additional combinatorial logic may large compared to the savings from needing less registers.
- Codes where only one or two bits change at a time in the state register may be beneficial.
- Less transitions may lead to less power depending on overall design, e.g. if stage register output connects to a high-capacitance load (high-fanout)
- Can minimize the chance of metastability errors (such as systems with tight timing, or radiation vulnerability).
- These codes may also minimize logic glitches.
FSM Log File
- The XST log file reports the full information of recognized Finite State Machine (FSM) components during the Macro Recognition step. Moreover, if you allow XST to choose the best encoding algorithm for your FSMs, it reports the one it chose for each FSM. \ As soon as encoding is selected, XST reports the original and final FSM encoding. If the target is an FPGA device, XST reports this encoding at the HDL Synthesis step. If the target is a CPLD device, then XST reports this encoding at the Low Level Optimization step.
Log File Example
Synthesizing Unit <fsm_1>. Related source file is "/state_machines_1.vhd". Found finite state machine <FSM_0> for signal <state>. ------------------------------------------------------ | States | 4 | | Transitions | 5 | | Inputs | 1 | | Outputs | 4 | | Clock | clk (rising_edge) | | Reset | reset (positive) | | Reset type | asynchronous | | Reset State | s1 | | Power Up State | s1 | | Encoding | automatic | | Implementation | LUT | ------------------------------------------------------ Found 1-bit register for signal <outp>. Summary: inferred 1 Finite State Machine(s). inferred 1 D-type flip-flop(s). Unit <fsm_1> synthesized. ========================================================
HDL Synthesis Report Macro Statistics # Registers : 1 1-bit register : 1 ======================================================== ======================================================== * Advanced HDL Synthesis * ======================================================== Advanced Registered AddSub inference ... Analyzing FSM <FSM_0> for best encoding. Optimizing FSM <state/FSM_0> on signal <state[1:2]> with gray encoding. ------------------- State | Encoding ------------------- s1 | 00 s2 | 01 s3 | 11 s4 | 10 ------------------- ======================================================= HDL Synthesis Report Macro Statistics # FSMs : 1 =======================================================
Constraints/Compiler Directives
- Most synthesizers support various instructions to modify synthesis behavior
- Many options can be applied globally or on a per module instance or even per block level.
- Some are entered in constraint files, as a command-line option or inline via special commented tags:
- The comment below is an example of a synthesizer directive / inline-constraint:
casex select // synthesis full_case 4'b1xxx: res = data1; 4'bx1xx: res = data2; 4'bxx1x: res = data3; 4'bxxx1: res = data4;
Xilinx FSM Constraints
- Xilinx Synthesis Constraints for state machines
- Related constraints are:
- fsm_extract
- determines if state machines are detected/extracted
- http://www.xilinx.com/itp/xilinx7/books/data/docs/cgd/cgd0093_54.html
- fsm_encoding
- can set state encoding globally or per-instance
- http://www.xilinx.com/itp/xilinx7/books/data/docs/cgd/cgd0092_53.html
- fsm_fftype
- use D or toggle flip flops for state register
- http://www.xilinx.com/itp/xilinx4/data/docs/cgd/f8.html
- enum_encoding
- sets encoding when fsm_extract is used to select user
- http://www.xilinx.com/itp/xilinx4/data/docs/cgd/e3.html
- fsm_extract
Default case
- You should notautomatically add default case to synthesize a FSM since the logic has to cover many unnecessary states
- Check documentation for your synthesizer's behavior
- http://www.trilobyte.com/pdf/golson_snug94.pdf
- Special effort may be required to have the synthesizer ignore the default case yet allow logging in simulation:
// synopsys translate_off default: \$display(“He’s dead, Jim.”) ; // synopsys translate_on
state variables
- Explicit States are stored in the state register, but other registers for variables can exist serving as extended state variables
- In-class example given
- Technically, every register in a digital system is a part of the state. What variables you decide to think of as state in your state diagram and what is coded in the CS register and used in the case statement is up to you.
- When there are many similar states, sometimes combining them in code and adding a register for a variable makes sense. This can reduce the state decoding and state logic and may make the code more maintainable and easier to read.
Additional Synthesis Options and Directives
http://www.xilinx.com/support/documentation/sw_manuals/xilinx11/pp_db_xst_hdl_synthesis_options.htm
Example state machine code if time allows
-
Example FFT Data Flow HW solution depicting extended state registers and state repetition